Operators
- Author:
Antonio J. Nebro
- Date:
2022-12-1
Evolutionary algorithms use selection and variation operators for getting the mating pool and for generate a descendant population from this pool, respectively. In the case of genetic algorithms, variation operators are mutation and crossover.
The Operator interface (package org.uma.jmetal.operator) belongs the jmetal-core sub-project, and it is defined as follows:
package org.uma.jmetal.operator;
/** Interface representing an operator
*
* @author Antonio J. Nebro <antonio@lcc.uma.es>
* @version 1.0
* @param <Source> Source Class of the object to be operated with
* @param <Result> Result Class of the result obtained after applying the operator
*/
public interface Operator<Source, Result> extends Serializable {
/**
* @param source The data to process
*/
Result execute(Source source) ;
}
According to this interface, an operator is a generic entity providing an execute() method
that is applied to a source and returns a result. The source and result are typically a solution
or a list of solutions, depending on the operator.
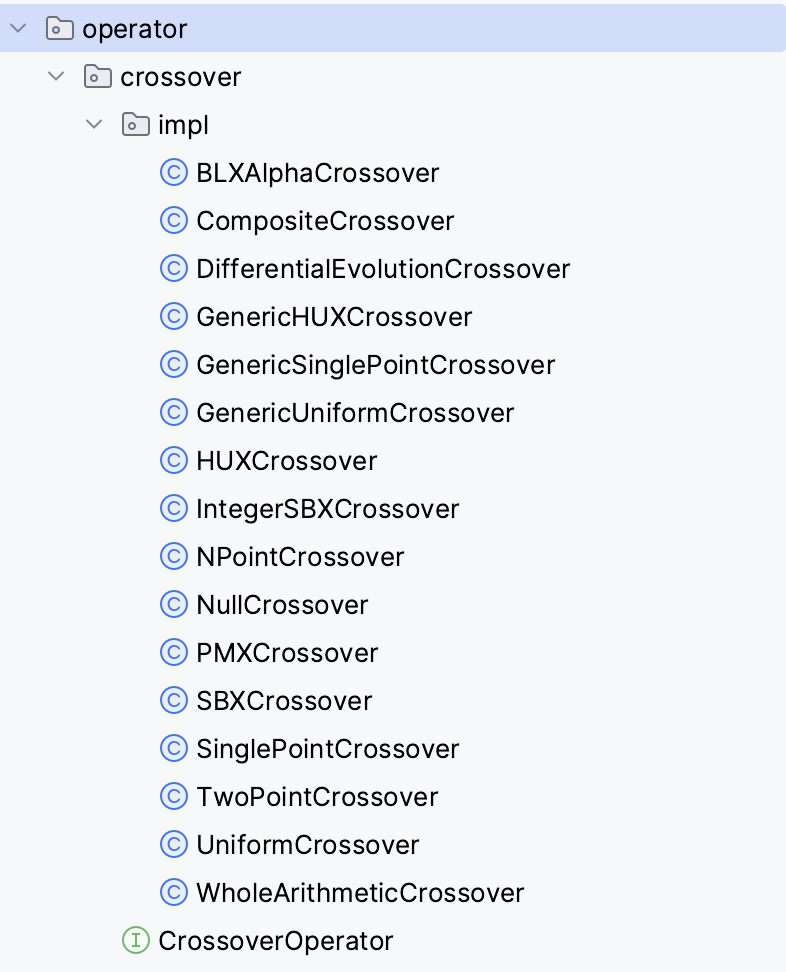
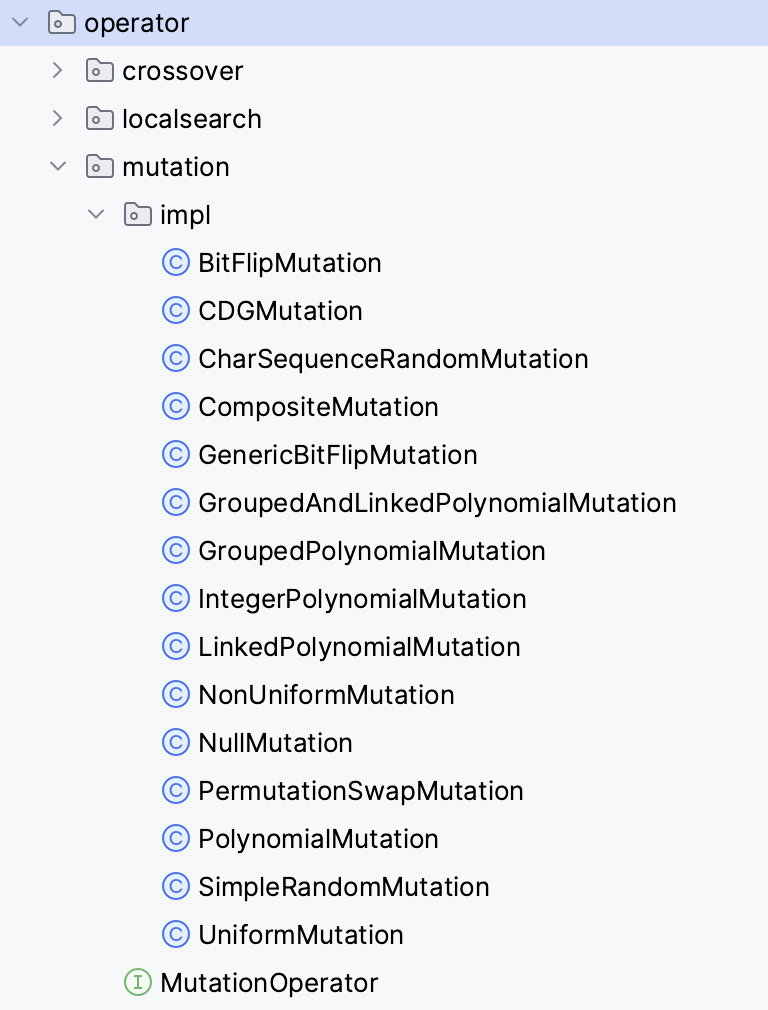
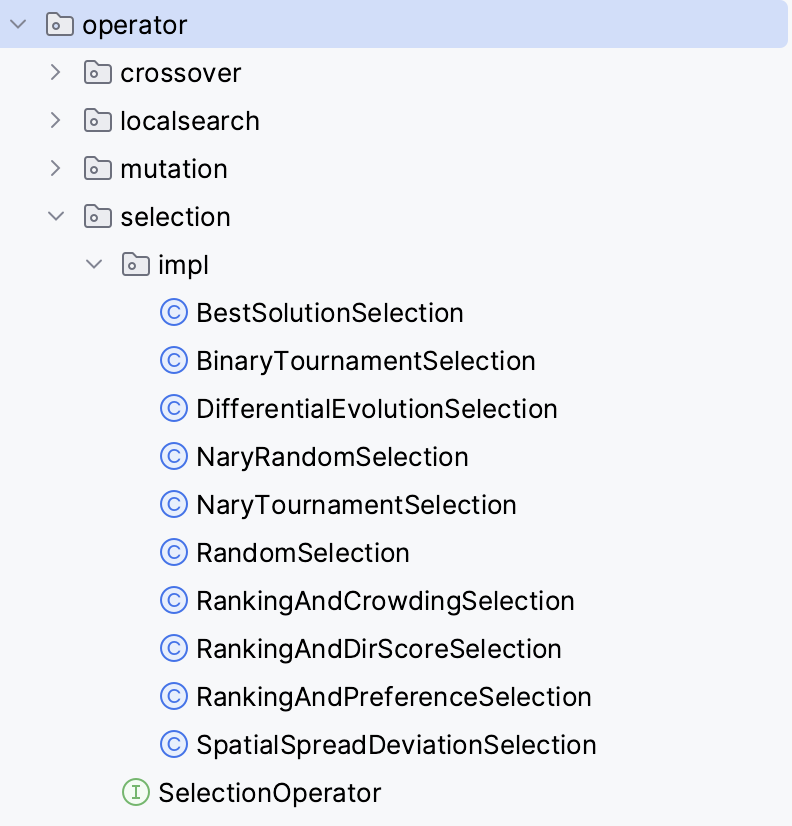
Four classes of operators are currently included:
Crossover. From a set of parent solutions, recombine them somehow to produce a number of children.Mutation. Mutates a solution.Selection. Select a number of solutions from a list according to some criterion.LocalSearchOperator. Applies a local search method to improve a solution.
In general, operators are related to the types of solutions to which they apply. For example, BLXAlphaCrossover is applied to DoubleSolution objects and its declaration is as follows:
public class BLXAlphaCrossover implements CrossoverOperator<DoubleSolution>
The currently implemented operators are included in the next figures: